02 스프링의 특징과 의존성 주입
스프링의 주요 특징
- POJO 기반의 구성
- 의존성 주입(DI)을 통한 객체간의 관계구성
- AOP 지원
- MVC구조
- WAS의 종속적 이지 않은 개발 환경
POJO 기반의 구성
- 별도의 API등을 사용하지 않는 POJO(Plain Old Java Object) 즉 일반적인 자바코드를 이용해서 객체를 구성하는 방식을 그대로 스프링에서 사용
의존성주입(DI)
-의존성이란?
하나의 객체 없이 제대로된 역할을 할수 X -> 주방방이 없으면 레스토랑이 운영할수 없다. (A가 B에 의존적이다.)
-주입 이란?
어떤 가게에서는 식재료를 구하기 위해 직접 시장에 가지만
프랜차이즈 음식점에서는 본사가 트럭을 이용해서 식재료를 공급한다. -> 객체를 얻기 위해 주체가 능동인지 수동인지
코드에서는 주입을 받는 입장에서는 어떤객체인지 신경쓸 필요가 없고 어떤 객체에 의존하든 자신의 역할은 변하지 않는다.

->의존성 주입방식을 이용하려면 위의그림과 같이
추가적인 하나의존재가 필요하다
이 존재는 의존성이 필요한 객체에 필요한 객체를 찾아서 주입하는 역할
즉. 스프링은 이러한 구조를 만드는데 적합한 구조로 설계되어 있다.
스프링에서는!
ApplicationContext라는 존재가 필요한 객체들을 생성하고 필요한 객체들을 주입해주는 역할을 해 주는 구조이다.
ApplicationContext가 관리하는 객체들을 Bean(빈)이라는 용어로 부르고
Bean과 Bean사이의 의존관계를 처리하는 방식으로
1. xml설정 2. 어노테이션 설정 3. Java설정을 이용할수 있다.
AOP의 지원 - 반복적인 코드의제거
스프링에서는 반드시 처리가 필요한 부분을 횡단 관심사(cross - concern)이라고 한다.이러한 횡단 관심사를 모듈로 분리하는것이 AOP이다.
트랜젝션의 지원 - 스프링은 트랜잭션의 관리를 어노테이션이나 XML로 설정 할수있다.
2.2 의존성 주입 테스트
[ex00프로젝트 먼저 ]
- 레스트로랑 객체를 만들고, 레스토랑에서 일하는 Chef객체를 주입
생성자 주입방법
- 스프링에서는 1.생성자를 이용, 2. setter메서드를 이용한 주입으로 의존성 주입을 구현한다.
설정방법은 주로 XML이나 어노테이션을 이용
예제는 Lombok을 이용해서 setter메서드를 자동으로 구현되게 할것이므로 -> pom.xml에서 Lombok라이브러리추가 ,spring-test라이브러리 이용
pom.xml에서 다음과 같이 수정한다
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
아래 코드를 추가한다.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
[jex00의 pom.xml]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.zerock</groupId>
<artifactId>controller</artifactId>
<name>jex00</name>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0.0-BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java-version>1.8</java-version>
<org.springframework-version>5.0.7.RELEASE</org.springframework-version>
<org.aspectj-version>1.6.10</org.aspectj-version>
<org.slf4j-version>1.6.6</org.slf4j-version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- Exclude Commons Logging in favor of SLF4j -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${org.aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- @Inject -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
<configuration>
<additionalProjectnatures>
<projectnature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</projectnature>
</additionalProjectnatures>
<additionalBuildcommands>
<buildcommand>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springbuilder</buildcommand>
</additionalBuildcommands>
<downloadSources>true</downloadSources>
<downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>org.test.int1.Main</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
예제 클래스 작성
ex00프로젝트에 'org.zerock.sample' 패키지를 작성한다.
Restaurant와 Chef클래스만든다.
package org.zerock.sample;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import lombok.Data;
@Component
@Data
public class Chef {
}
Restaurant는 Chef클래스를 주입받도록 설계
package org.zerock.sample;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.Setter;
@Component //스프링에서 해당 클래스가 관리해야할 대상(Bean)임을 표시
@Data //lombok의 setter생성기능, 생성자와 toString()을 자동으로 생성
public class Restaurant {
//@Setter에서 사용된 onMethod 속성은 생성되는 setChef()에 @Autowired어노테이션을 추가하도록 한다.
@Setter(onMethod_ = @Autowired) //생성자나 세터 등을 사용하여 의존성주입을 하려고 할때 해당 bean을 찾아서 주입해주는 annotation이다.
private Chef chef;
}
짜잔
XML을 통한 의존성 주입 설정
- 스프링에서 관리되는 객체를 Bean이라고 하고, 이에대한 설정은 XML과 Java를 이용해서 처리 할수 있다.
root-context.xml 은 Bean(객체) 을(를) 설정하는 설정 파일이다.

context항목을 체크한뒤
source탭을 클릭
<beans></beans>사이에 아래코드 추가한다.
<context:component-scan base-package="org.zerock.sample">
</context:component-scan>
그러면 하단 bean graph에서 Restaurant객채와 Chef객체가 생성된 것을 볼 수있다.

[Java 설정을 이용하는 의존성 주입]
root-context.xml 대신 RootConfig.class 를 이용한다.
XML로 설정된 내용은 @ComponentScan어노테이션을 통해 처리 한다.
package org.zerock.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"org.zerock.sample"})
public class RootConfig {
}
스프링이 동작하면서 생기는일
스프링이동작하면서 일어나는 일들을 시간의 순서대로 알아보면

- 스프링 프레임워크가 시작되면 스프링이 사용하는 메모리영역을 만든다.(Context) ->스프링에서는 ApplicationContext라는이름의 객체가 만들어진다.
- 스프링은 자신이 객체를 생성하고 관리해야하는 객체들에대한 설정이 필요한데 root-context.xml 파일이다.
- root-context.xml 에 설정되어있는 <context:component - scan>태그의 내용을 통해 'org.zerock.sample'패키지를 scan하기 시작한다.
- 해당 패키지에 있는 클래스들중 스프링이 사용하는 @Component라는 어노테이션이 존재하는 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성
- Restaurant객체는 Chef객체가 필요하다는 어노테이션(@Autowired)설정이 있으므로 스프링은
Chef객체의 레퍼런스(참조변수) 를 Restauant객체에 주입한다.
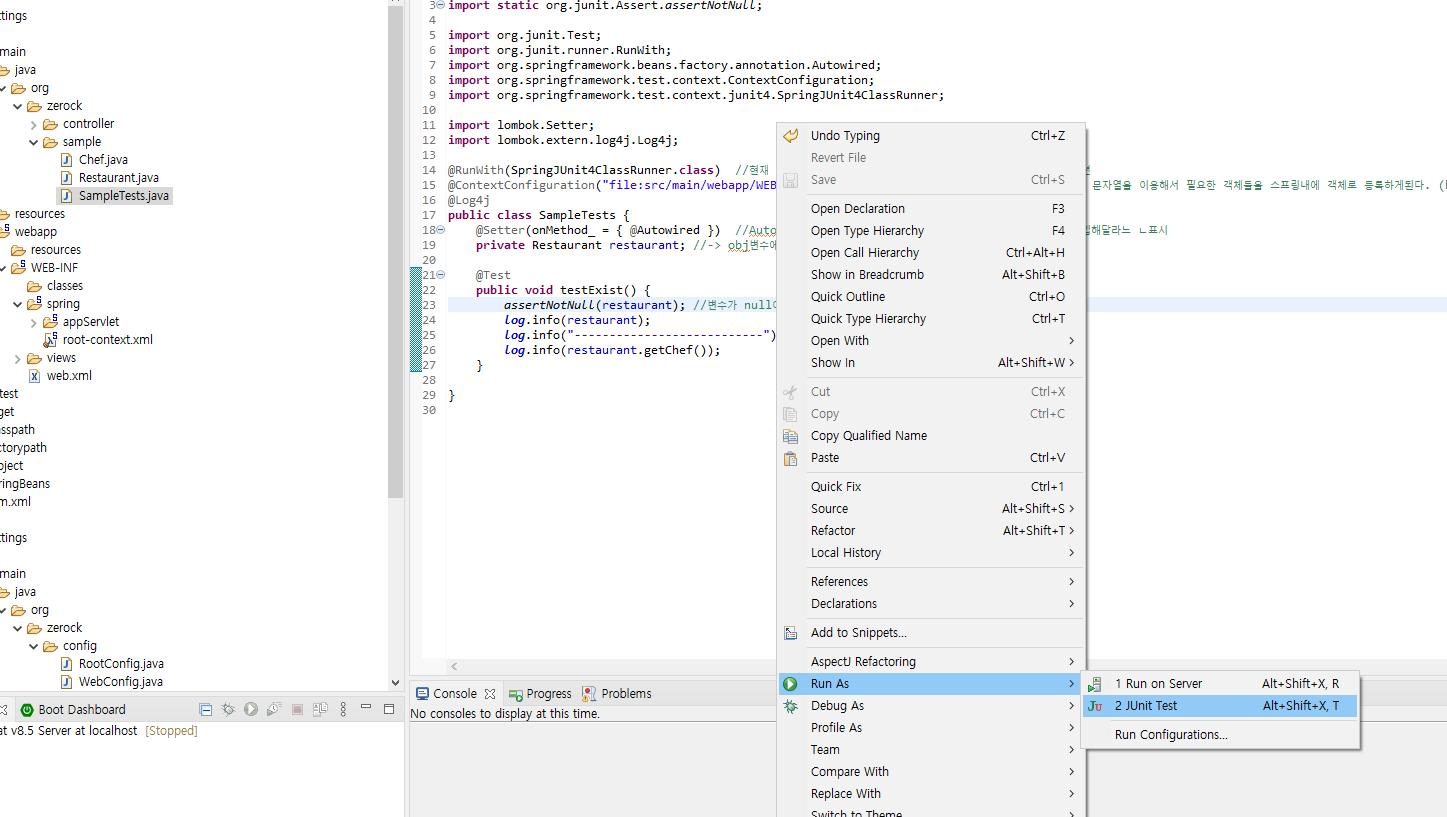
[ex00]
package org.zerock.sample;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //현재 테스트코드가 스프링을 실행하는 역할을 할것이라는 ㄴ어노테이션
@ContextConfiguration("file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml") //지정된 클래스나 문자열을 이용해서 필요한 객체들을 스프링내에 객체로 등록하게된다. (bean으로 동록된다고표현)
@Log4j
public class SampleTests {
@Setter(onMethod_ = { @Autowired }) //Autowired 는 해당인스턴스 변수가 스프링으로 부터 자동으로 주입해달라느 ㄴ표시
private Restaurant restaurant; //-> obj변수에 Restaurant타입의 객체를 주입
@Test
public void testExist() {
assertNotNull(restaurant); //변수가 null이 아니여야먄 test가 성공함을 의미
log.info(restaurant);
log.info("---------------------------");
log.info(restaurant.getChef());
}
}

[jex00]
Java를 이용하는 경우의 테스트 설정
테스트에서 사용한 @ContextConfiguration어노테이션은 XML뿐만 아니라 Java설정을 이용할 때도 사용할 수있다.
SpringJUnit4ClassRunner 빨간줄
pom.xml에 spring-test라는 이름의 의존성을 주입해 줘야함
Tip - @Autowired를 setter보다 먼저 임포트
package org.zerock.sample;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.zerock.config.RootConfig;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes= {RootConfig.class})
@Log4j
public class SampleTests {
@Setter(onMethod_ = { @Autowired})
private Restaurant restaurant;
@Test
public void testExist() {
assertNotNull(restaurant);
log.info(restaurant);
log.info("--------------------------");
log.info(restaurant.getChef());
}
}
어노테이션
-Lombok관련
value - 접근제한속성
onMethod - setter메서드의 색성시 메서드에 추가할 어노테이션을 지정
onParam - setter메서드의 파라미터에 어노테이션을 사용하는경우에 적용
@Data
는 @ToString @EqualsAndHashCode , @Getter/@Setter, @RequiredArgsConstructor를 모두 결합한 형태로 한번에 자주 사용되는 모든 메서드들을 생성할수 있다 ->세부적인 설정이 필요없는경우사용
@Log4j
로그 객체를 생성
- Spring 관련
@Component
해당 클래스가 스프링에서 객체로 만들어서관리하는 대상임을 명시하는 어노테이션
->@Component가 있는 클래스를 스프링이 읽어주도록 @ComponentScan을 통해서 지정되어있으므로 해당 패키지에 잇는 클래스 들을 조사하면서 @Component 가 존재하는 클래스들을 객체로 생성해서 빈으로 관리하게된다.

@Autowired
- 자신에게 해당 타입의 bean을 주입해달라는 표시
테스트 관련 어노테이션
@ContextConfiguration
스프링이 실행되면서 어떤 설정 정보를 읽어 들여야하는지를 명시
속성으로는 locations를 이용하여 문자열의배열로 XML 설정 파일을 명시 할수 도 있고
classes속성으로 @Configuration 이 적용된 클래스를 지정해 줄수 도 있다.
@RunWith
테스트시 필요한 클래스 지정
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@Test는 junit에서 해당 메서드가 junit상에서 단위테스트의 대상인지 알려준다.
'web' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코드로 배우는 스프링 웹프로젝트 - 04 MyBatis와 스프링 연동 (0) | 2020.09.30 |
|---|---|
| 코드로 배우는 스프링웹프로젝트 -JDBC테스트코드 (0) | 2020.09.29 |
| 코드로 배우는 스프링웹프로젝트 - 스프링과 Oracle Database연동 (0) | 2020.09.29 |
| 코드로 배우는 스프링웹 프로젝트 03 (0) | 2020.09.29 |
| 코드로 배우는 스프링 웹프로젝트 01 (0) | 2020.09.28 |